Cations And Anions Chart
Salts are compounds composed of cations bonded to anions.
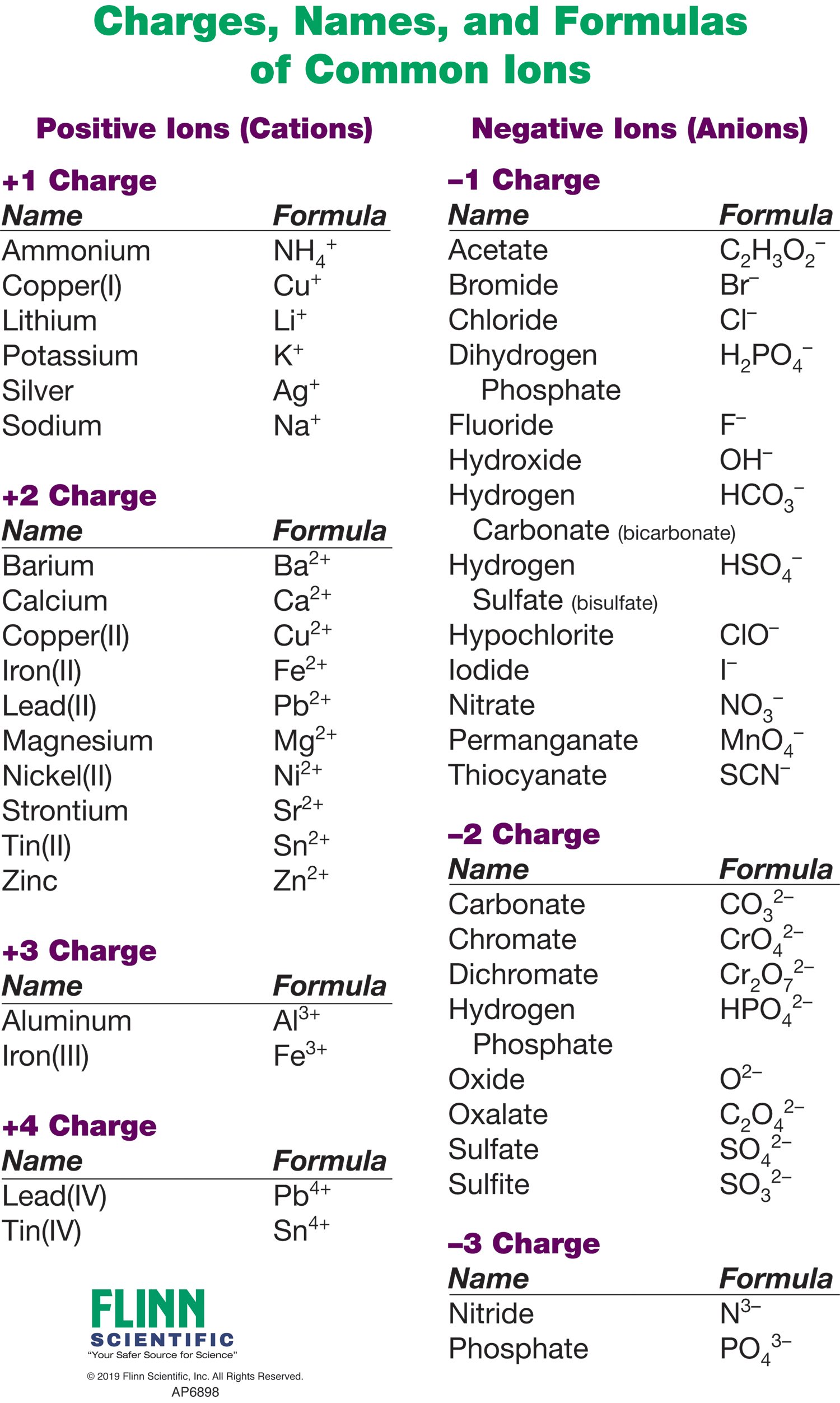
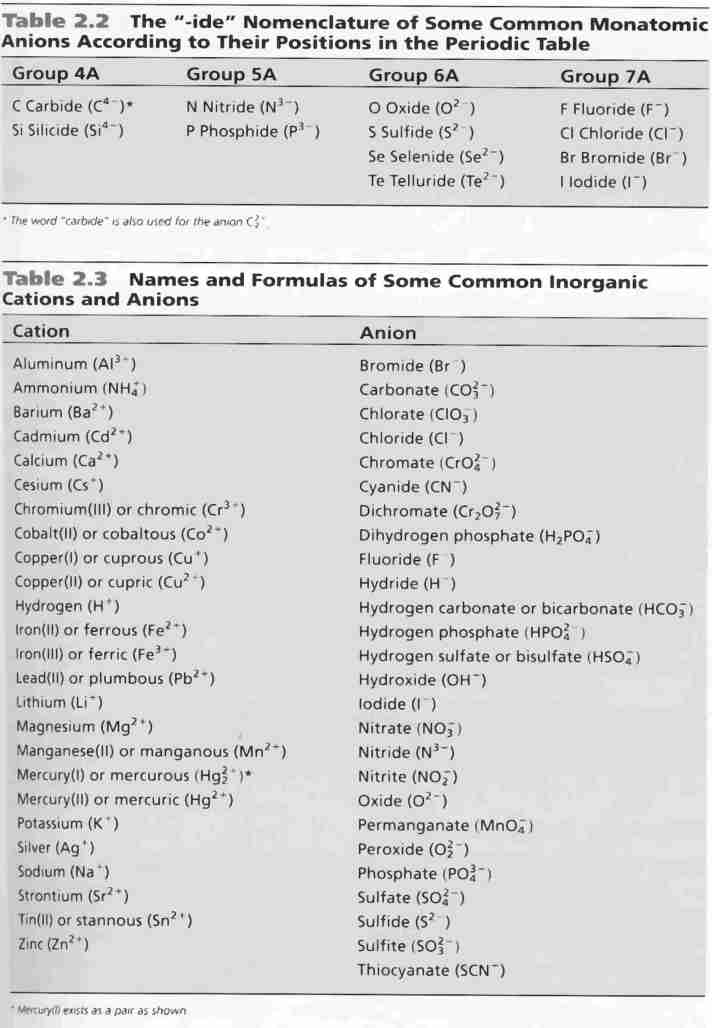
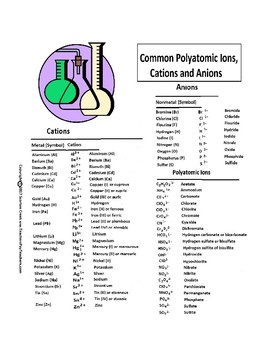
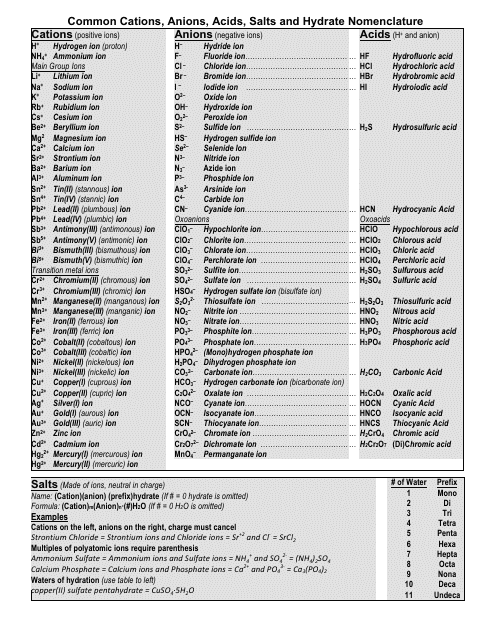
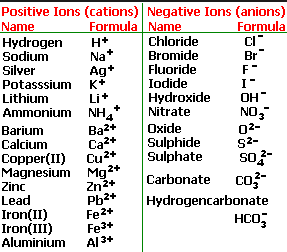
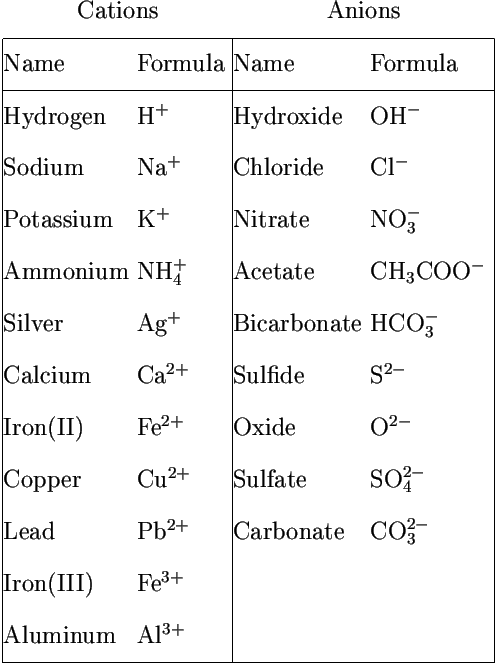
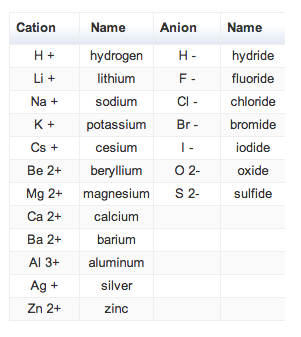
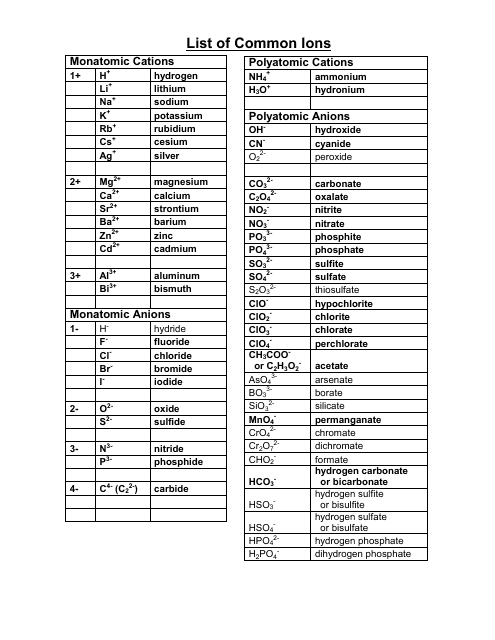
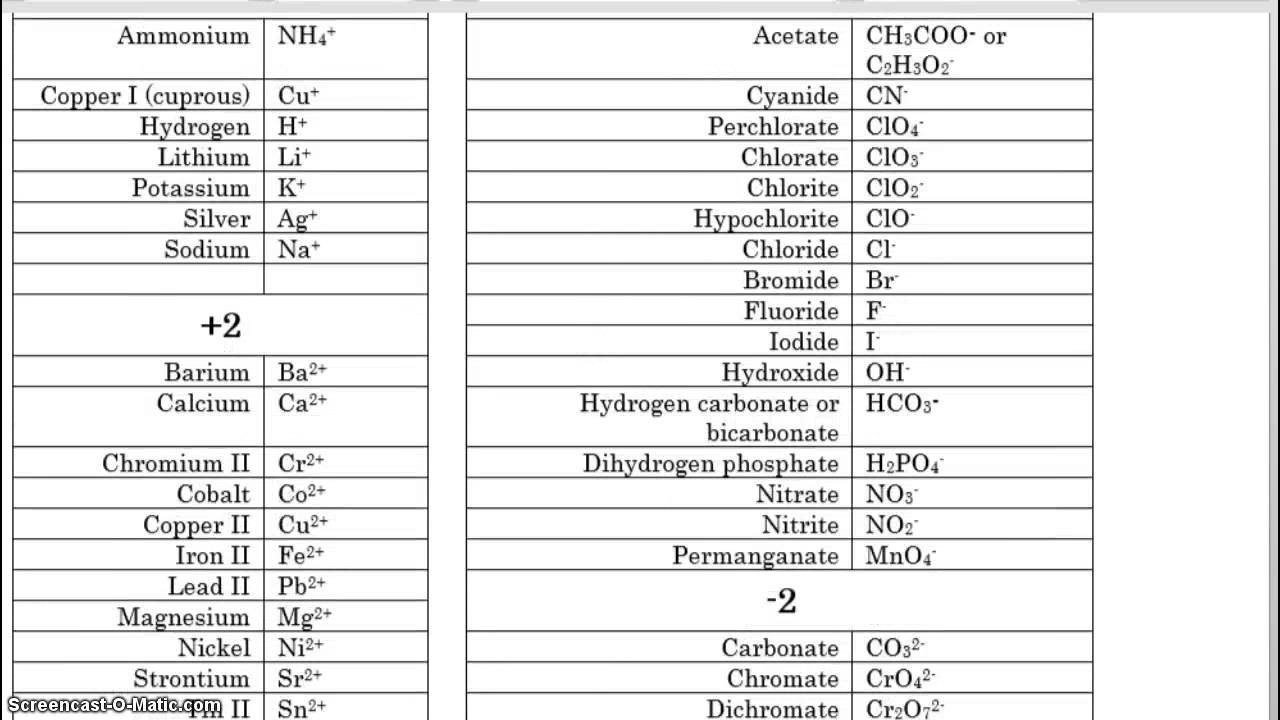
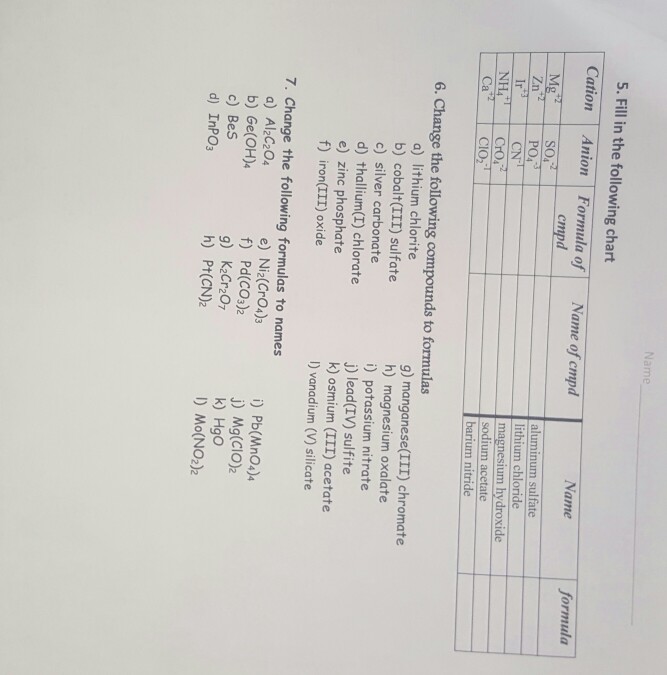
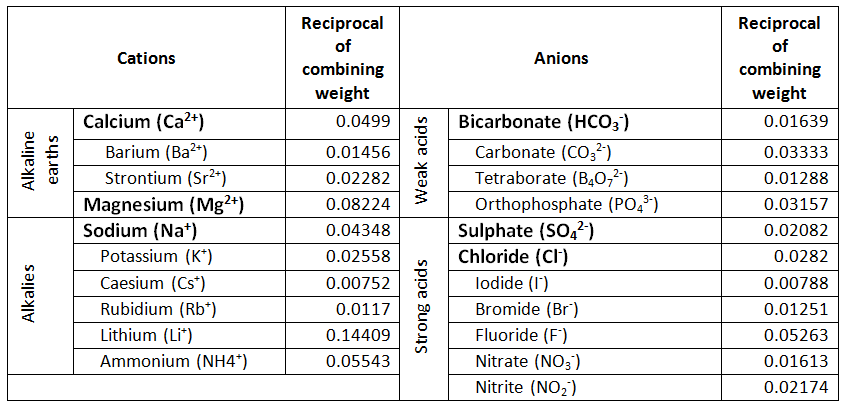
Cations and anions chart. Roman numeral notation indicates charge of ion when element commonly forms more than one ion. Ferrocyanide fe cn 6 4 pyrophosphate p2o7 4 silicate sio4 4 silicide si 4 3. Key differences between cation and anion.
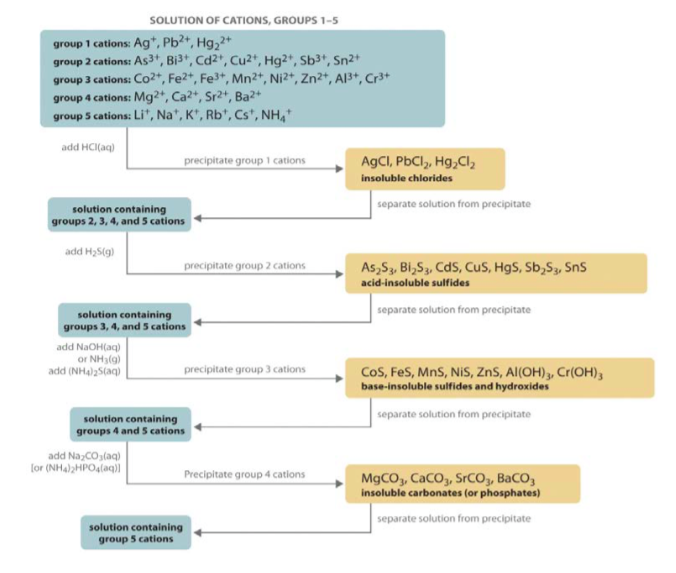
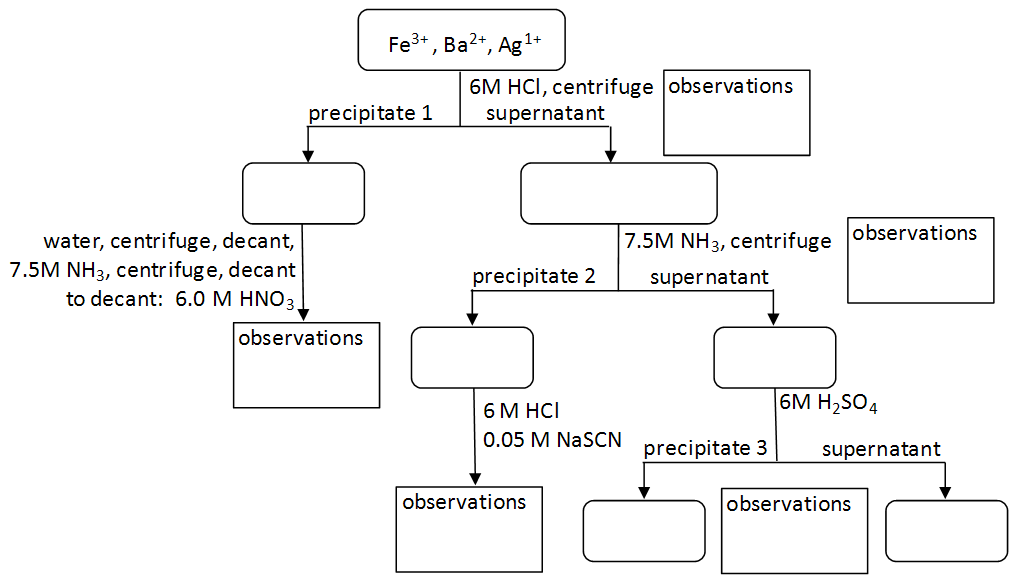
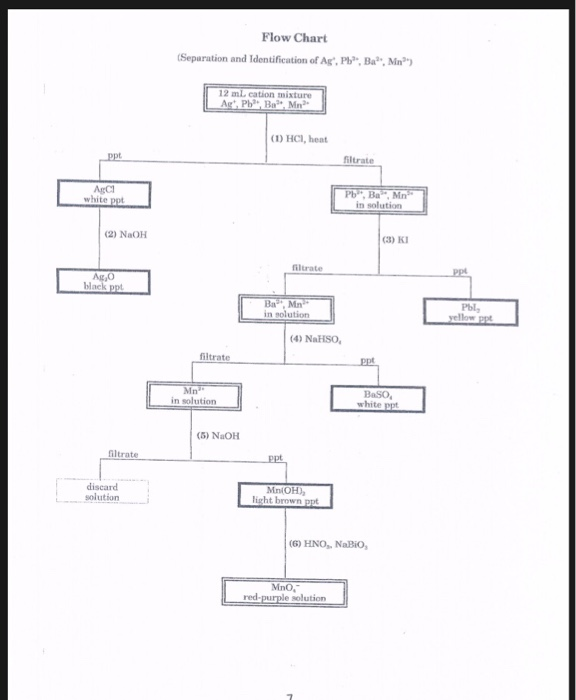
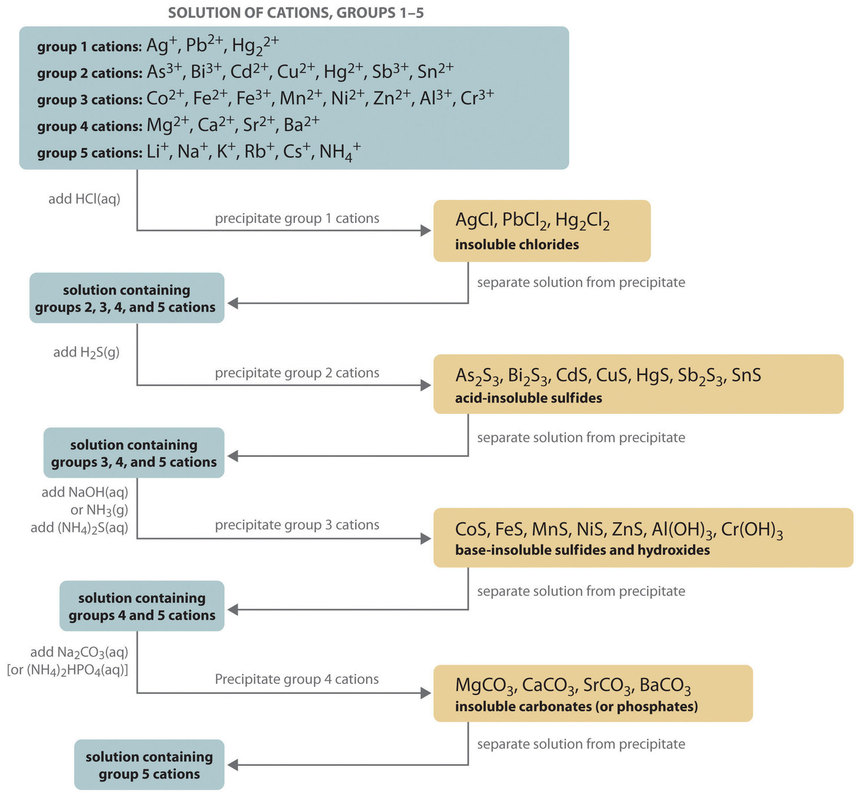
The resulting compound carries a neutral electrical charge. For example iron ii has a 2 charge. To understand the rationale and the procedure behind the separation for various cations and anions.
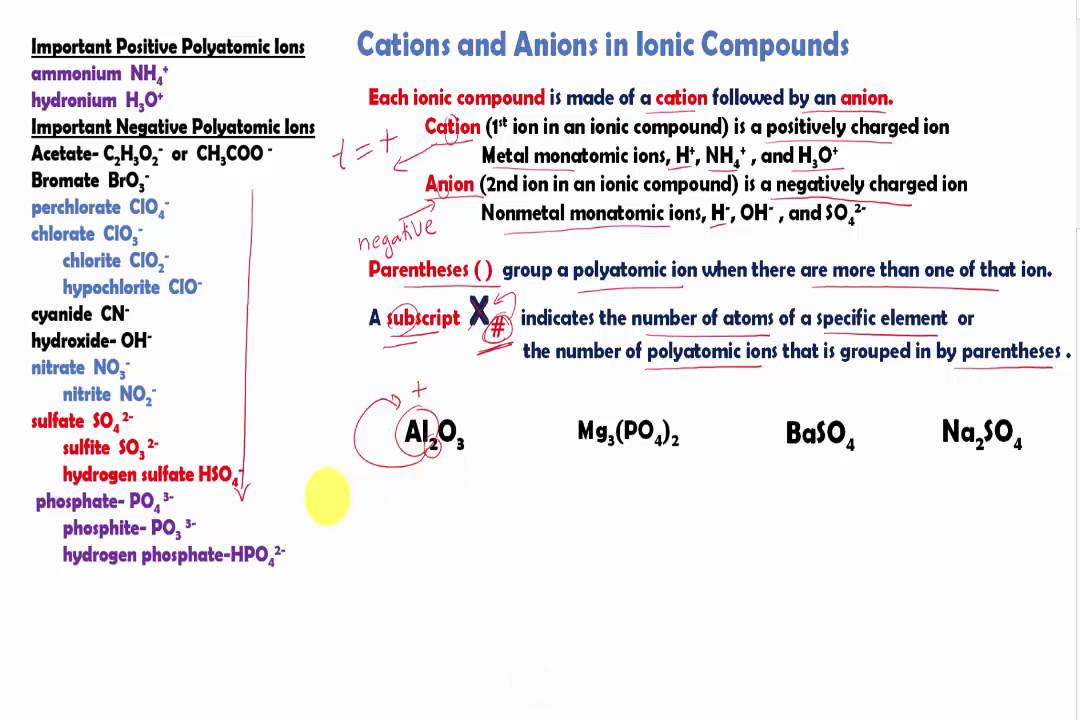
Chlorine cl gains one electron to become cl whilst oxygen o gains two electrons to become o 2. The number of electrons gained and so the charge of the ion is indicated after the chemical symbol e g. For example table salt or sodium chloride consists of the na cation bonded to the cl anion to form nacl.
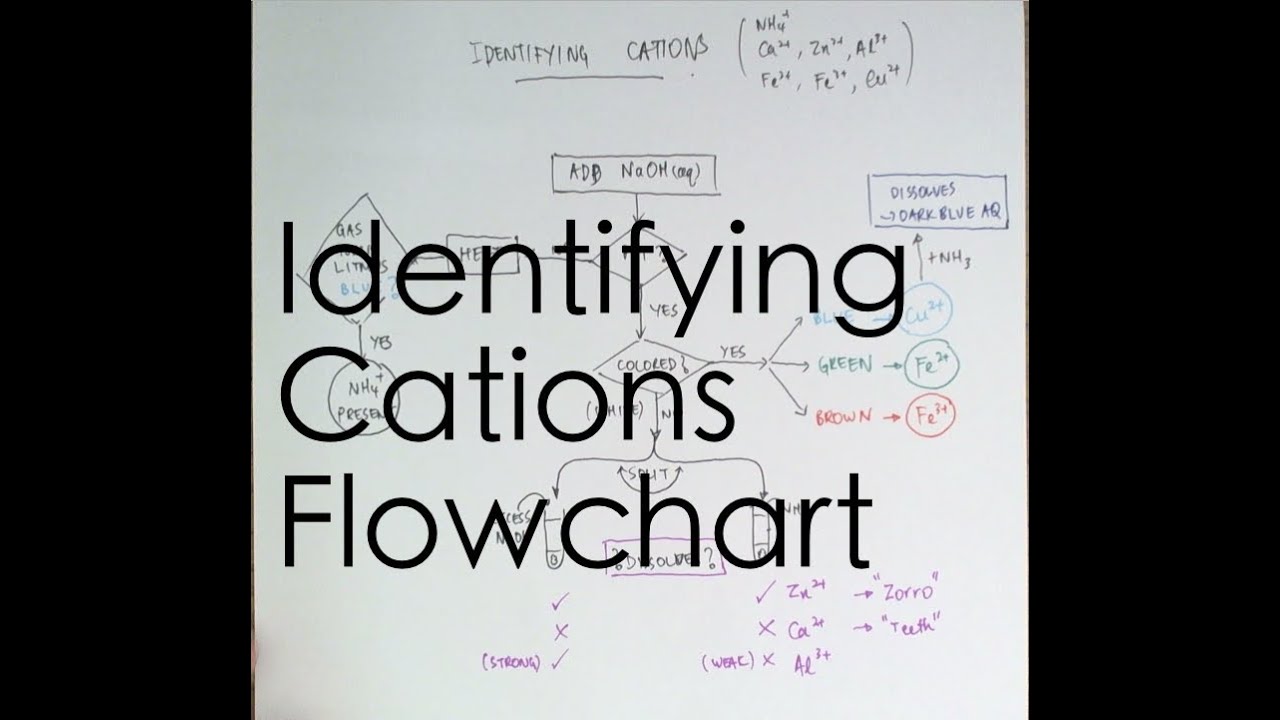
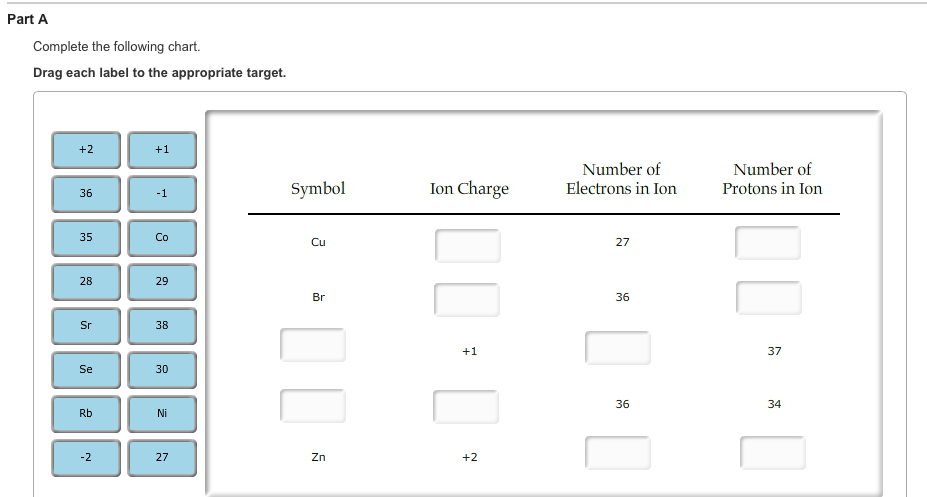
An ion may consist of a single atom of an element a monatomic ion or monatomic cation or anion or of several atoms that are bonded together a polyatomic ion or polyatomic cation or anion because of their net electrical charge cations are repelled by other cations and are attracted to anions. Cations are ions which have a positive electrical charge a cation has fewer electrons than protons. Qualitative analysis of cations and anions objectives.
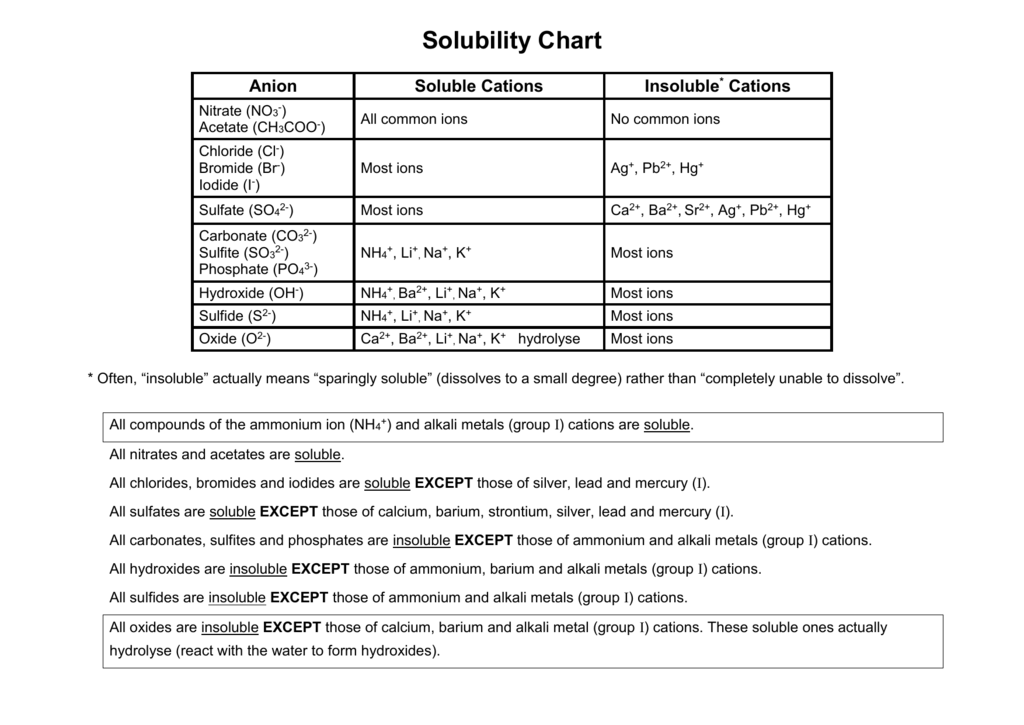
Salts are hygroscopic or tend to pick up water this water is called water of hydration. So an atom or molecule having more number of protons than electrons and are positively charged is called cation while an atom or molecule having more number. The net charge gained by an ion of an atom or atoms is the fundamental phenomena to separate the and anion.
Anion versus cation comparison chart. A cation is an atom or a molecule which is positively charged i e. An anion is an atom or a molecule which is negatively charged i e.
Complete list of cation and anions. Given below are the essential points which differentiate the cations to that of anions. Has more number of electrons than protons.
To perform qualitative analysis of two unknown solutions that contain various ions cations and anions and positively identify these ions using established schemes. The main differences between cations and anions are summarized in the table below. Antimonide sb 3 arsenate aso4 3 arsenide as 3 borate bo3 3 boride b 3 citrate c6h5o7 3 hypophosphite po2 3 nitride n 3 perphosphate po5 3 phosphate po4 3 phosphide p 3 phosphite po3 3.
Iron iii a 3 charge. Cation vs anion chart.